RCW 49 (NGC 3247)
Whirling Dervish Nebula. HII Region, Carina
- Description
- Technical
- Links
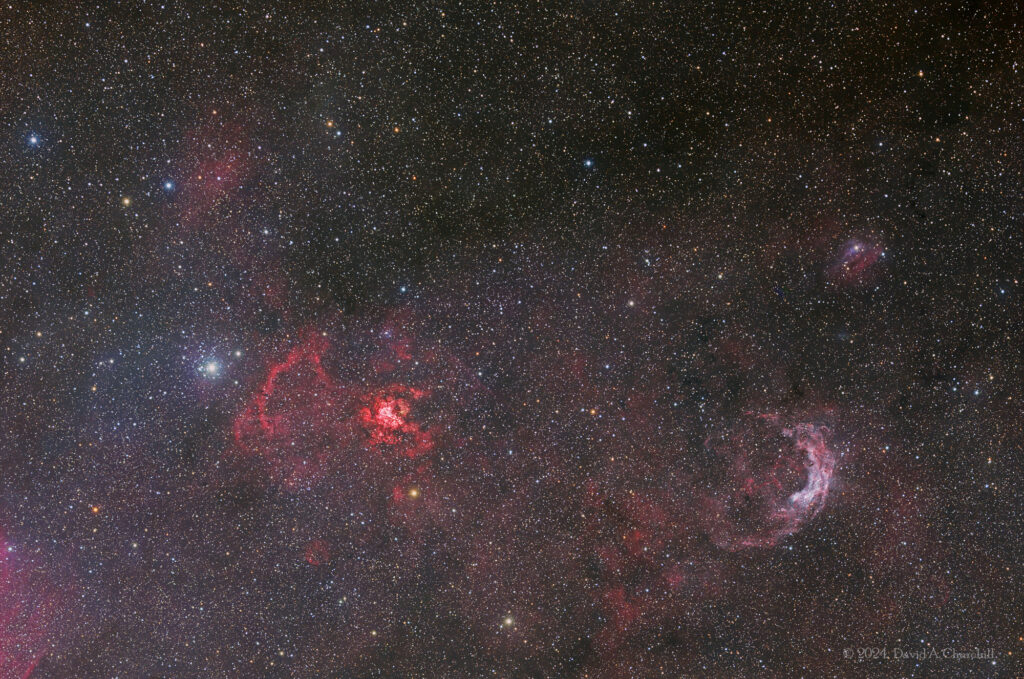
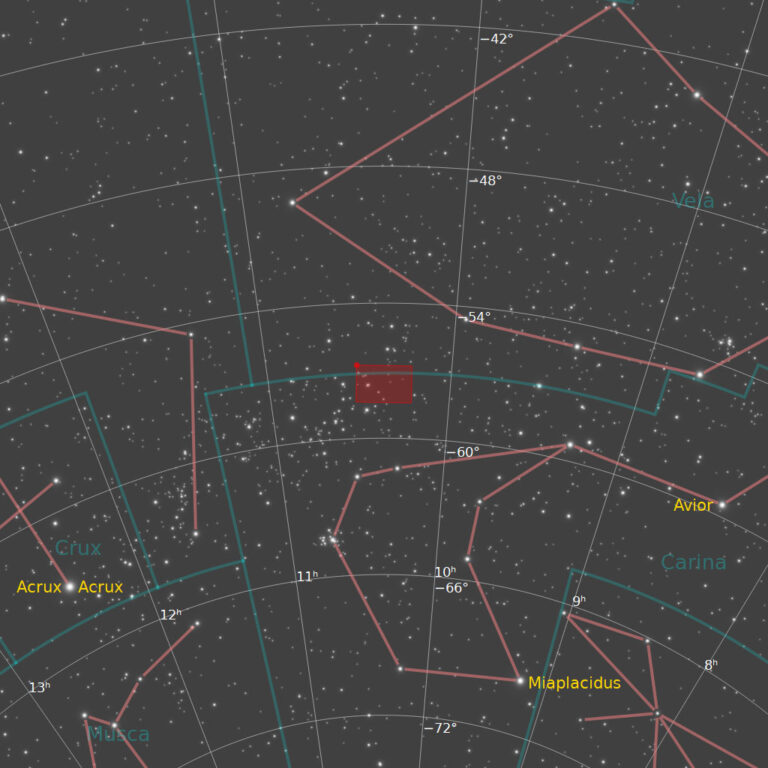
RCW 49, also known as NGC 3247, is a H II region nebula located 13,700 light years away in the constellation of Carina. Other designations for the RCW 49 region include NGC 3247 and Gum 29 and it is commonly known as the Whirling Dervish Nebula. It is a dusty stellar nursery that contains more than 2,200 stars and is about 300-400 light years across. RCW 49 is recognized as among the brightest and most massive HII regions.
In 2004, a 2003 image by the Spitzer Space Telescope was released showing the nebula in infrared wavelengths. This included an image showing the infrared colors mapped to visible light colors: 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (green), 5.8 microns (orange) and 8 microns (red). It was noted as being almost 14 thousand light years from Earth, and the infrared camera could detect the stars obscured by dust clouds. It was estimated at least 200 of the stars in the nebula have dust disks. The results of observations of the Spitzer Telescope, including the IRAC camera, have been studied leading to the conclusion that the region is a star-forming region. In 2014, RCW 49 was identified as a bow shock candidate, along with M17 in a study of Extended Red Objects (ERO’s) and Stellar Wind Bow Shocks in the Carina nebula.
The RCW Catalogue (from Rodgers, Campbell & Whiteoak) is an astronomical catalogue of Hα-emission regions in the southern Milky Way, described in (Rodgers et al. 1960). It contains 182 objects, including many of the earlier Gum catalogue (84 items) objects. The later Caldwell catalogue included some objects from the RCW catalogue. There is also some overlap with the Sharpless catalogue-2 (312 items), although that primarily covered the northern hemisphere, whereas RCW and Gum primarily covered the southern hemisphere. The RCW catalogue was compiled by Alexander William Rodgers, Colin T. Campbell and John Bartlett Whiteoak. They catalogued southern nebulae while working under Bart Bok at the Mount Stromlo Observatory in Australia in the 1960s.
In 2004, a 2003 image by the Spitzer Space Telescope was released showing the nebula in infrared wavelengths. This included an image showing the infrared colors mapped to visible light colors: 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (green), 5.8 microns (orange) and 8 microns (red). It was noted as being almost 14 thousand light years from Earth, and the infrared camera could detect the stars obscured by dust clouds. It was estimated at least 200 of the stars in the nebula have dust disks. The results of observations of the Spitzer Telescope, including the IRAC camera, have been studied leading to the conclusion that the region is a star-forming region. In 2014, RCW 49 was identified as a bow shock candidate, along with M17 in a study of Extended Red Objects (ERO’s) and Stellar Wind Bow Shocks in the Carina nebula.
The RCW Catalogue (from Rodgers, Campbell & Whiteoak) is an astronomical catalogue of Hα-emission regions in the southern Milky Way, described in (Rodgers et al. 1960). It contains 182 objects, including many of the earlier Gum catalogue (84 items) objects. The later Caldwell catalogue included some objects from the RCW catalogue. There is also some overlap with the Sharpless catalogue-2 (312 items), although that primarily covered the northern hemisphere, whereas RCW and Gum primarily covered the southern hemisphere. The RCW catalogue was compiled by Alexander William Rodgers, Colin T. Campbell and John Bartlett Whiteoak. They catalogued southern nebulae while working under Bart Bok at the Mount Stromlo Observatory in Australia in the 1960s.
Telescope: Astro Physics 155EDF (TCC) f5.4
Mount: Astro Physics 1600GTO
Camera: FLI PL29050 / CFW2-7
Guider: Agena Starguide II / ZWO ASI178MM
Filters: Astrodon II 50mm LRGB
L: 53×10 mins = 530 mins, R: 20×10 mins = 200 mins, G: 24×10 mins = 240 mins, B: 24×10 mins = 240 mins
Total Imaging Time: 20h 10m
Data Imaged remotely on 8 nights during February & March 2024.
Imaged from Observatorio El Sauce, Chile, in partnership with Fred Espenak.
Data acquisition & Processing by David Churchill.
None