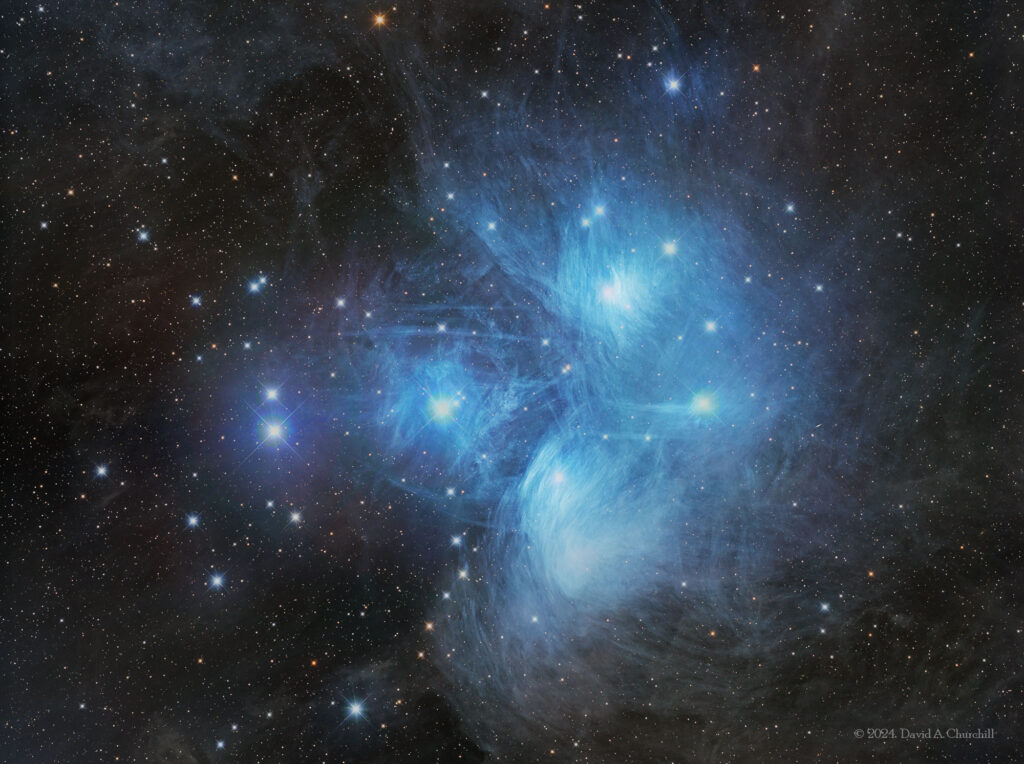
Messier 45
The Pleiades, Open Star Cluster with Reflection Nebula. Taurus
September 2024. Cave Creek Canyon Observatory, Arizona Sky Village
- Description
- Technical
- Links
The Pleiades, also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance of about 444 light years, it is among the nearest star clusters to Earth. It is the nearest Messier object to Earth, and is the most obvious cluster to the naked eye in the night sky. It is also observed to house the reflection nebula NGC 1432, an HII Ionized region. The cluster is dominated by hot blue luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Reflection nebulae around the brightest stars were once thought to be left over material from their formation, but are now considered likely to be an unrelated dust cloud in the interstellar medium through which the stars are currently passing. This dust cloud is estimated to be moving at a speed of approximately 18 km/s relative to the stars in the cluster. Computer simulations have shown that the Pleiades were probably formed from a compact configuration that resembled the Orion Nebula. Astronomers estimate that the cluster will survive for about another 250 million years, after which it will disperse due to gravitational interactions with its galactic neighborhood.
The name of the Pleiades comes from Ancient Greek. It probably derives from plein (“to sail”) because of the cluster’s importance in delimiting the sailing season in the Mediterranean Sea: “the season of navigation began with their heliacal rising”. However, in mythology the name was used for the Pleiades, seven divine sisters, the name supposedly deriving from that of their mother Pleione and effectively meaning “daughters of Pleione”. In reality, the name of the star cluster almost certainly came first, and Pleione was invented to explain it. The Pleiades are a prominent sight in winter in the Northern Hemisphere, and are easily visible out to mid-Southern latitudes. They have been known since antiquity to cultures all around the world. The earliest-known depiction of the Pleiades is likely a Northern German Bronze Age artifact known as the Nebra sky disk, dated to approximately 1600 BC. The Babylonian star catalogues name the Pleiades MULMUL, meaning “stars” (literally “star star”), and they head the list of stars along the ecliptic, reflecting the fact that they were close to the point of vernal equinox around the 23rd century BC. The Ancient Egyptians may have used the names “Followers” and “Ennead” in the prognosis texts of the Calendar of Lucky and Unlucky Days of papyrus Cairo 86637. Some Greek astronomers considered them to be a distinct constellation, and they are mentioned by Hesiod’s Works and Days, Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey, and the Geoponica. The Pleiades was the most well-known star among pre-Islamic Arabs and so often simply referred to as “the Star” (al Najm). Some scholars of Islam suggested that the Pleiades (ath-thurayya) are the “star” mentioned in Surah An-Najm (“The Star”) in the Quran. In Japan, the cluster is mentioned under the name Mutsuraboshi (“six stars”) in the 8th-century Kojiki. The cluster is now known in Japan as Subaru.
The Pleiades have long been known to be a physically related group of stars rather than any chance alignment. John Michell calculated in 1767 that the probability of a chance alignment of so many bright stars was only 1 in 500,000, and so surmised that the Pleiades and many other clusters of stars must be physically related. When studies were first made of the stars’ proper motions, it was found that they are all moving in the same direction across the sky, at the same rate, further demonstrating that they were related. Charles Messier measured the position of the cluster and included it as M45 in his catalogue of comet-like objects, published in 1771. Along with the Orion Nebula and the Praesepe cluster, Messier’s inclusion of the Pleiades has been noted as curious, as most of Messier’s objects were much fainter and more easily confused with comets—something that seems scarcely possible for the Pleiades. One possibility is that Messier simply wanted to have a larger catalogue than his scientific rival Lacaille, whose 1755 catalogue contained 42 objects, and so he added some bright, well-known objects to boost his list. The nine brightest stars of the Pleiades are named for the Seven Sisters of Greek mythology: Sterope, Merope, Electra, Maia, Taygeta, Celaeno, and Alcyone, along with their parents Atlas and Pleione. As daughters of Atlas, the Hyades were sisters of the Pleiades.
The name of the Pleiades comes from Ancient Greek. It probably derives from plein (“to sail”) because of the cluster’s importance in delimiting the sailing season in the Mediterranean Sea: “the season of navigation began with their heliacal rising”. However, in mythology the name was used for the Pleiades, seven divine sisters, the name supposedly deriving from that of their mother Pleione and effectively meaning “daughters of Pleione”. In reality, the name of the star cluster almost certainly came first, and Pleione was invented to explain it. The Pleiades are a prominent sight in winter in the Northern Hemisphere, and are easily visible out to mid-Southern latitudes. They have been known since antiquity to cultures all around the world. The earliest-known depiction of the Pleiades is likely a Northern German Bronze Age artifact known as the Nebra sky disk, dated to approximately 1600 BC. The Babylonian star catalogues name the Pleiades MULMUL, meaning “stars” (literally “star star”), and they head the list of stars along the ecliptic, reflecting the fact that they were close to the point of vernal equinox around the 23rd century BC. The Ancient Egyptians may have used the names “Followers” and “Ennead” in the prognosis texts of the Calendar of Lucky and Unlucky Days of papyrus Cairo 86637. Some Greek astronomers considered them to be a distinct constellation, and they are mentioned by Hesiod’s Works and Days, Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey, and the Geoponica. The Pleiades was the most well-known star among pre-Islamic Arabs and so often simply referred to as “the Star” (al Najm). Some scholars of Islam suggested that the Pleiades (ath-thurayya) are the “star” mentioned in Surah An-Najm (“The Star”) in the Quran. In Japan, the cluster is mentioned under the name Mutsuraboshi (“six stars”) in the 8th-century Kojiki. The cluster is now known in Japan as Subaru.
The Pleiades have long been known to be a physically related group of stars rather than any chance alignment. John Michell calculated in 1767 that the probability of a chance alignment of so many bright stars was only 1 in 500,000, and so surmised that the Pleiades and many other clusters of stars must be physically related. When studies were first made of the stars’ proper motions, it was found that they are all moving in the same direction across the sky, at the same rate, further demonstrating that they were related. Charles Messier measured the position of the cluster and included it as M45 in his catalogue of comet-like objects, published in 1771. Along with the Orion Nebula and the Praesepe cluster, Messier’s inclusion of the Pleiades has been noted as curious, as most of Messier’s objects were much fainter and more easily confused with comets—something that seems scarcely possible for the Pleiades. One possibility is that Messier simply wanted to have a larger catalogue than his scientific rival Lacaille, whose 1755 catalogue contained 42 objects, and so he added some bright, well-known objects to boost his list. The nine brightest stars of the Pleiades are named for the Seven Sisters of Greek mythology: Sterope, Merope, Electra, Maia, Taygeta, Celaeno, and Alcyone, along with their parents Atlas and Pleione. As daughters of Atlas, the Hyades were sisters of the Pleiades.
Telescope: Planewave Delta Rho 350 f3.0
Mount: Astro Physics 3600GTO “El Capitan”
Camera: ZWO ASI461MM pro / EFW-7
Guider: ZWO OAG-L-68 / ZWO ASI174mm Mini
Filters: Astrodon II 50mm Sq LRGB
L: 68×5 mins = 340 mins, R: 25×5 mins = 125 mins, G: 36×5 mins = 180 mins, B: 36×5 mins = 180 mins
Total Imaging Time: 13h 45m
Data Imaged remotely on 8 nights during September 2024.
Data acquisition & Processing by David Churchill.
None